Cutting: –
Separation of part of the plant and planting it in the media suitably and developing it as a new plant is called cutting.
Watch Lecture Video
Types of Cutting
- Stem Cutting: –
Creating new plants by taking some part from the stem is called stem cutting.
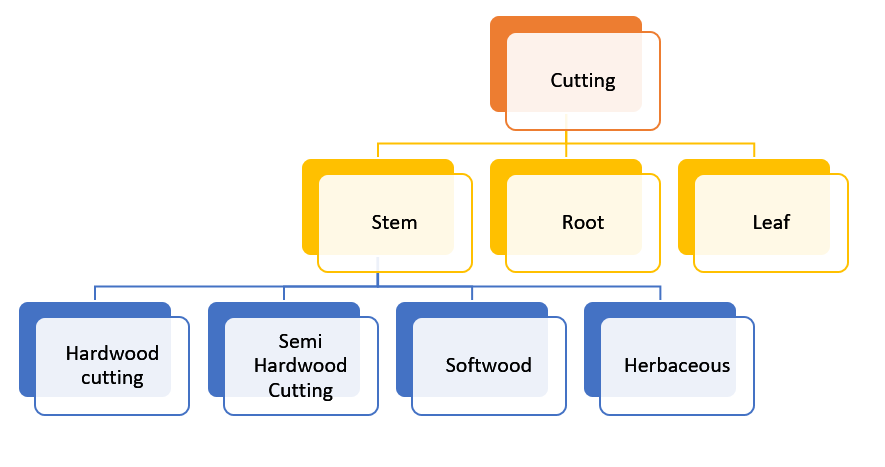
i). Hard Wood Cutting –
In this method, the cutting is taken from a woody branch of a year or elder. The cutting should not be taken from a branch with high Vigorous Growth and long internode. Cutting length 10–45 cm. should be kept. A cutting with two to three buds, which is cut from near the bottom bud and 1 to 2 cm above the top bud. The top cut on the cutting should be slanting. Due to the slanting top, the water does not stop over the cut when irrigation. The cutting should be treated with a solution of 1500 ppm IBA before planting, which leads to quicker root development. The cutting should be made from November to February. This type of cutting is made in grapes, figs, pomegranate mulberry, rose, etc.
ii). Semi-Hard Wood Cutting –
The cutting is taken from a semi-hard wooden branch of 4-9 months old. The length of the cutting should be 7-20 cm. The entire leaves are removed, leaving the top 2-3 leaves of the cutting. This type of cutting should be made in the rainy season. When there is high humidity in the atmosphere. After treatment with PGR, it is planted in a prepared nursery bed. This cutting is made in mango, guava, jackfruit, lemon, aonla, etc.
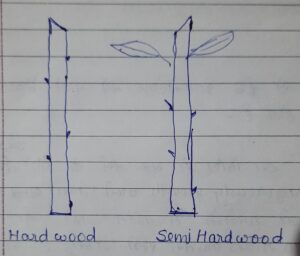
iii) Soft Wood Cutting –
This type of cutting is not commonly used in the propagation of fruit trees. And there should be more humidity when making cutting. The cutting should be taken from a 2-3 months old branch. The length of the cutting should be kept at 10–15 cm. This type of cutting is prepared in apple, pear, guava, and some ornamental plants.
iv) Herbaceous Cutting –
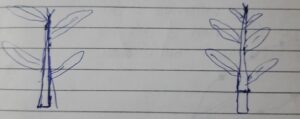
Ornamental plants are usually propagated with herbaceous cutting. The cutting is made from a 1-2 months old branch. The leaves are cut off from the base of the cutting and the upper leaves are allowed to remain, as the carbohydrate accumulated in the branch is low and the leaves are used to make food. This cutting is used in the propagation of Alternanthera, Coleus piles, Iresine.
2. Root Cutting –
Plants that produce suckers can be easily propagated with root cutting. Cutting 10–15 cm long are prepared from 2-3 cm thick roots. For root cutting preparation the best season is December for temperate fruits and the rainy season for sub-tropical fruits. The cutting should be treated with hormones before sowing. The prepared cutting is planted directly in the field.
3. Leaf Cutting –

Generally, the ornamental and succulents plant can be propagated with leaf cuttings. Buds are found in the thick leaves of the succulents plants. Leaves from such plants are cut and planted in the nursery. Plants can be prepared by leaf-cutting in Begonia, Sansevieria, Crassula, etc.
References cited
1.Chadha, K.L. Handbook of Horticulture (2002) ICAR, NewDelhi
2.Jitendra Singh Basic Horticulture (2011) Kalyani Publications, New Delhi
3.K.V.Peter Basics Horticulture (2009) New India Publishing Agency
4. Jitendra Singh Fundamentals of Horticulture, Kalyani Publications, New Delhi
