Nursery
A nursery is a place where plants are prepared by various propagation methods and taken care of until they are suitable for planting in the field. There are two types of nurseries.
Watch Lecture Video
Types of Nursery
1. Permanent Nursery
Great care is taken in the construction of a permanent nursery, the road location for the nursery is chosen and such nursery should be close to the city. Labour and water should be available throughout the year. Structures like shed house, glasshouse, a cold frame, hotbed etc. are built in the nursery. Surround walls or thorny plant fences are planted to protect the nursery. In such nurseries, beds are paved and modern techniques of irrigation are also used such as overhead irrigation, etc. Such nurseries produce high-value fruit trees and ornamental plants.
2. Temporary Nursery
Temporary nurseries are built in the shade of trees. Permanent beds are not made in this. Such a nursery is prepared for annual flowering plants and vegetables such as: – Tomato, Brinjal, Onion, Cabbage, Marigold, Cosmos, etc.
Benefits of Raising Nursery
- More plants can be grown easily in less space in the nursery.
- Due to less space, suitable climatic conditions can be easily provided to the plants. While it is not possible to provide such facilities in open conditions.
- Due to less area, diseases and pests can be easily controlled.
- In the nursery, the production of off-season vegetable plants nursery can be taken and produced in a controlled environment.
- Seed can be given a suitable environment in the nursery so that their germination is good.
- Proper use of land can be done in the nursery.
- Every resource of the nursery like labour, water, nutrients is properly utilized.
- The production of some vegetables is increased after their nursery raise and transplanted.
- Yield can be increased by choosing uniform and healthy plants from the nursery.
- More plants can be grown in the nursery at a lower cost.
Selection of Site and Location
The following points should be kept in mind while choosing the place.
- Should choose an open and safe place.
- Do not choose a place that is close to a large building.
- The shady location is not suitable for a nursery.
- There should be a proper drainage facility in the nursery area.
- There should be a permanent water supply in the nursery area.
- Workers in the nursery should be available throughout the year.
- The place should be connected by road, from which the plant can be easily transported.
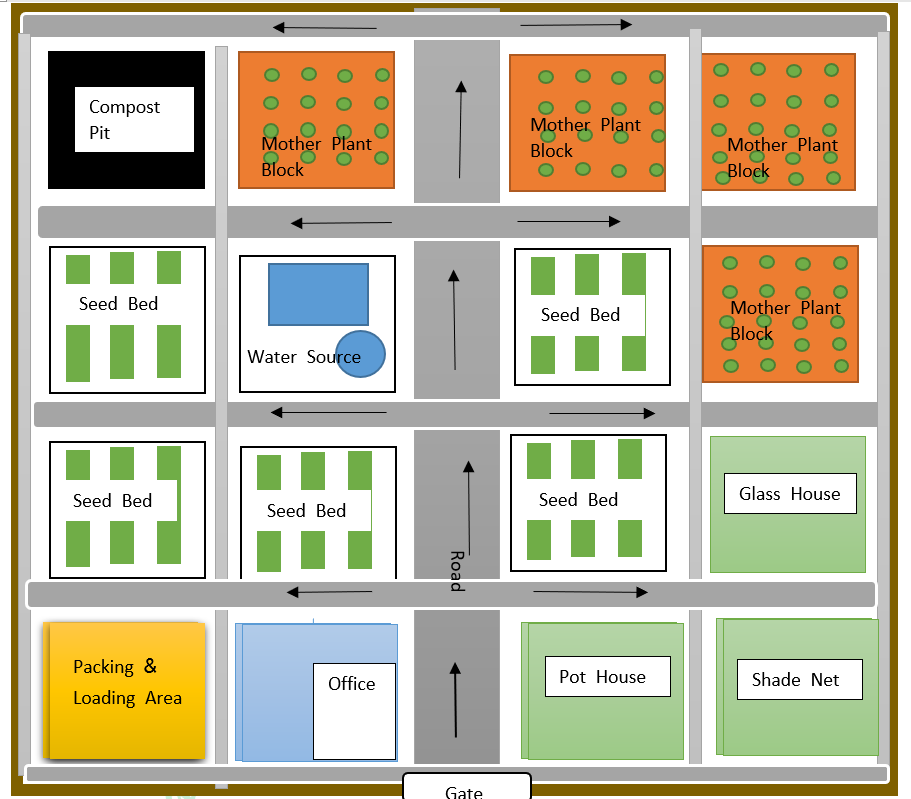
Parts of Nursery
-
Seed Bed
The beds in which seeds are sown are called seedbeds. Cuttings are also planted in these beds. Such beds are constructed in shade areas to reduce the water requirement in the plants and always keep moisture in the bed.
The length of the beds is kept as per requirement but the width is not kept more than 1 to 1.5 meters as there is a problem in agricultural activities like weeding etc.
The nursery also has some deep beds which are used for placing plants in polythene bags. The depth of these beds is 30 cm. Due to being deep, after giving water to the bags, the moisture remains for a long time due to the sun not falling straight. Seedbeds are three types
A) Flat Nursery Bed
In areas where there is no rain during the spring and summer seasons or the soil is light sandy to sandy loam and the water does not stop, such types of beds are made in those areas.
For the construction of these beds, the field soil is first ploughed by plough two or three times. In this good rotten FYM of 10 kg per square meter mixed in the last ploughing. The field is then divided into beds of required length and 1 to 1.5 meters wide. The ridge is made around the bed and an irrigation channel is made between the two beds.
B) Raised Nursery Bed
Such beds are commonly used for sowing seeds in nurseries. Raised beds are also beneficial during rainy days. In heavy soil, more problems of damping-off are found during the rainy days. So this type of bed is made 10-15 cm raise from the ground. Pebbles, stone, roots of plants, etc. are removed from the soil while constructing the bed, Good rotten FYM of 10 kg per square meter is mixed. Between the lines of two beds, 50-60 cm distance is kept. Which is used in cultural operations such as irrigation, weeding, etc.
C) Sunken Nursery Bed
Deep beds are more useful in the summer season. Such beds are made 10-15 cm deep from the ground so that the plants can also survive in the cold air. In winter, the bed can also be covered with a sheet of polythene.
-
Mother Plant Block
Each nursery should have a mother plant block. By which parts of plants can be found for cutting, budding, grafting, etc. Mother plants should have the following characteristics
- Trees should be of good quality.
- Their variety should be known and liked in that area, particularly by farmers.
- Trees should be high-yielding.
- These trees should be free from pests and diseases.
-
Packing Yard
The packing yard is the main part of the nursery where the plants are prepared for sale. So that they can be easily transported from one place to another. The packing yard should be close to the office. And it should be connected to the road. In which the packing material like box, rope, thread, polythene, etc. should be available at all times.
-
Pot House
The rootstock for inarching is prepared in pots or in polythene bags. In addition, some ornamental plants are also planted in pots which are kept in a pot-house. So, the pothouse is built in a shady place in the nursery. Can also be prepared from the shade net.
-
Compost Pit
Manure is always required in the nursery. So a pit is dug for manure in one corner of the nursery, in which the garbage, leaves, etc. of the nursery are put which are used as manure after decomposition.
-
Water Source
The nursery has a permanent source of water as new plants in the nursery require daily irrigation. Therefore, the source of water is made in the middle of the nursery so that water can be reachable to each part of the nursery. According to the facility in the nursery, tube well, well or tanks, etc. are made.
Figure:- Ideal Nursery Layout
References cited
1.Chadha, K.L. Handbook of Horticulture (2002) ICAR, NewDelhi
2.Jitendra Singh Basic Horticulture (2011) Kalyani Publications, New Delhi
3.K.V.Peter Basics Horticulture (2009) New India Publishing Agency
4. Jitendra Singh Fundamentals of Horticulture, Kalyani Publications, New Delhi
