Horticulture Guruji
Exercise 11
To study the micro-propagation in fruit crops
HORT 111
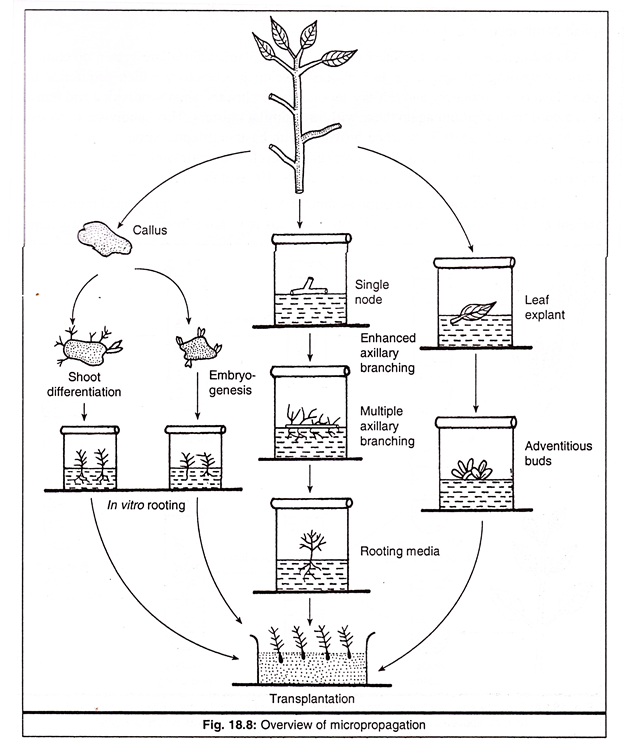
Micropropagation:- Micropropagation (tissue culture or invitro culture) refers to the multiplication of plants, in aseptic conditions and in artificial growth mediums from plant parts like meristem tip, callus, embryos, anthers, axillary buds, etc.
It is a method by which a true to type and disease-free entire plant can be regenerated from a miniature piece of plant in the aseptic condition in an artificial growing medium rapidly throughout the year.
Merits of micropropagation:
- Tissue culture helps in the rapid multiplication of true-to-type plants throughout the year.
- A new plant can be regenerated from a miniature plant part, whereas, in conventional methods, a shoot of considerable length is required.
- The large number of plants can be produced in culture tubes in small spaces with uniform growth and productivity instead of growing them in large areas in the nursery.
- Plants raised by tissue culture are free from diseases.
- Tissue culture coupled with somatic hybridization (production of hybrid cells by fusion of two protoplasts with different genetic makeup.)helps in evolving new cultivars in a short time.
- Micropropagation facilitates long-distance transport of propagation materials and long-term storage of clonal materials.
- Tissue culture methods are particularly effective in plants that don‘t breed true from seeds, seeds are not viable (male sterile) or not available (banana) and in-plant where propagation by conventional methods are expensive (Orchids)
Demerits of Micropropagation:
- The cost involved in setting up and maintenance of a laboratory is very high and may not justify their use in all the horticultural plants ordinarily.
- Tissue culture techniques require skilled manpower.
- Slight infection may damage an entire lot of plants.
- Some genetic modification (mutation) of the plant may develop with some varieties and culture systems, which may alter the quality of the produce.
- The seedlings grown under artificial conditions may not survive when placed under normal environmental conditions.
Methods of Micropropagation: Different methods of micro-propagation are Meristem culture, Callus culture, Cell culture, Embryo culture, Protoplast culture, Shoot apex grafting, and Pollen grain culture.
References cited
- Commercial Fruits. By S. P. Singh
- A text book on Pomology, Vol,1. by T. K. Chattapadhya
- Tropical Horticulture, Vol.1, by T. K. Bose, S. K. Mitra, A. A. Farooqui and M. K. Sadhu